In this article, we'll be looking into the development stages of a blockchain and understand how it works, its use cases, and much more! Let's dig in!!!🙌
TESTNET 🚀
A testnet (test network) is an experimental network where developers can test, create, or modify functionalities and monitor the blockchain network performance.
A testnet (testing environment) is where the features or functionalities of a coin or token are used by the developers or test engineers for testing purposes. They fix bugs and other kinds of network failures. They reuse test files to ensure an accurate comparison between test runs. This sandbox environment enables the developers to take risks, experiment, and find out the best possible model, a stable version, to be implemented in the mainnet. All these happen at scale in a controlled manner. Let’s dig deeper to get more understanding of this network:
Importance of testnet ⏳
Testnet serves many important functions including:
Continuous development:
Blockchain technology is still in its infancy and requires a great deal of testing and development to gradually come to mainstream and authorized use. Testnet’s environment was created to cater to this.
For example, one of the main issues being solved in the blockchain community is scalability. Ongoing research and development will enhance blockchain’s ability to handle more transactions. In order to continuously improve the capabilities of blockchain, many tests on smart contract functionality, transactions, and mining processes must be conducted. Testnet serves as a simulation of how the actual blockchain protocol (mainnet) works in real life.
Safe for mainnet:
Testnet allows testers and application developers to test the features and functionality of the protocol in a separate environment without having to worry about breaking the main blockchain. Doing tests on the mainnet is not possible because the complex interactions between components in the protocol can damage the network or break the main chain. This will cause a major disruption to the blockchain and may weaken the protocol. Therefore, this is a common practice for projects running prototypes on testnet first, to resolve specifications and ensure that everything is in the right order.
Free trial:
For blockchain to enable smart contract functionality, the network’s own cryptocurrency must be used to perform the deliveries. For example, ether (ETH) is a payment request for calculations that occur within the Ethereum blockchain network.
It will be very costly for developers to test application features
or run tests on the mainnet, as they will need to purchase large
quantities of cryptocurrencies with real value. Testnets
provides a testing platform for developers who want to create
applications on the blockchain or test certain functions at no
charge.
Ethereum Testnet Examples 🤔
TESTNET USE CASES 🤫
- Development in a safe environment.
- A testnet sandbox provides a secure environment for testing various development ideas.
- Minimal disruptions.
- Blockchain teams are aggressively trying to resolve problems around scalability, security, and decentralization.
- Numerous tests are being performed and prototypes are run on the cryptocurrency testnet without disrupting the mainnet.
- Any decentralized applications (dApps) which want to onboard, need to go through a phase of testing and fixes.
- New patches, features, etc are first tested in the testnet.
- Some examples of these tests include security tests, load testing, blockchain migration, integration tests, and disaster recovery.
- Testnet allows for faster and safer launching of a mainnet.
EXAMPLE
💭
Before deploying to the mainnet, we can use the test network to ensure everything is working fine. We can choose the blockchain on which we want to work and the test network. For ethereum, if you need a stable testnet with support on multiple clients go with goerli. If you need to have conditions as close as possible to mainnet, but less stability than goerli, choose ropsten.
Mainnet 🚀
A Mainnet (main network) is the final, most stable, and fully functional version of the blockchain. Mainnet enables dApps to be launched for public use. They see an increased number of validators who are incentivized by tokens with real value. All transactions are live on the mainnet. Projects with a mainnet are considered more mature. It gives users the confidence that the project has put lots of effort and resources into the blockchain. This is because the mainnet has gone through rigorous evaluation processes before it launched its mainnet.
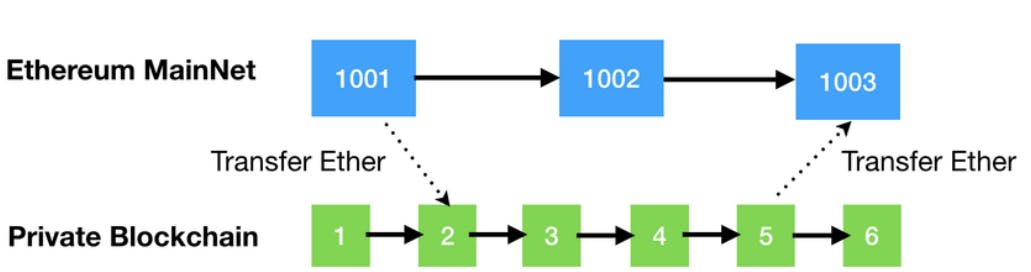
TRIALS + TESTNET = MAINNET
As a fully functioning blockchain, mainnets can be used to send and receive any transaction, in the form of cryptocurrency or non-fungible tokens (NFTs) among others, or transform information.
Importance of mainnet ⏳
- It is the final product of blockchain projects that makes it possible to send and receive digital currencies.
- In the mainnet, transactions are being broadcasted, verified, and recorded on a distributed ledger technology (Blockchain).
- The tokens on a mainnet hold a monetary value.
- Mainnet increases the value of an asset.
Before the mainnet launch of the blockchain project, the team of that particular project will set up an initial coin offering (ICO), an initial exchange offer, or any other means that can help the project to raise funds which are then used to develop the prototypes of the blockchain network, which is then tested during the testnet phase. After performing bug fixes and depending on the performance of the testnet, the team will then launch the mainnet version of the blockchain, which is ideally fully deployed and functional.
MAINNET USE CASES 🤫
- The mainnet acts as proof that the blockchain is functional.
- It gives an open invitation to the public to participate in the network.
- Before launching a mainnet, a blockchain already partners with application creators. Hence some of those applications launch along with the mainnet launch. This provides use cases for further dApps to onboard the blockchain.
- Most blockchains make the underlying codes public after the crypto mainnet launch. Such open-source projects become more credible to users.
- The permissionless public network enables discovery.
- Additional mainnet features like security properties for example anti-spam capabilities can be availed.
What is the Difference Between a Testnet and a Mainnet? 🧠
- Purpose: The testnet is the testing “Sandbox”, whereas the mainnet is the released functional blockchain.
- Cost of Operations: In the testnet, the tokens do not hold any value. The cost of operations on the mainnet is higher. Every operation performed on the blockchain requires a fee in the form of tokens that hold a certain value. Examples of these operations include transfers of value, staking rewards, or deployments of smart contracts.
- Network ID: The network ID helps developers identify the network. Mainnets and testnets have different network IDs. For example, the Ethereum mainnet network ID is 1, while the other most commonly used testnets have network IDs of 3, 4, and 42 for ropsten, rinkeby, and kovan, respectively.
- Genesis Block: A genesis block is the first block of every blockchain. Both testnets and mainnets have their own independent genesis blocks.
- Nodes: A testnet has fewer nodes than a mainnet.
- Transaction Frequency: Transaction frequency is low for a testnet.
Mainnet vs Testnet on the Matic Network 👀
A testnet and a mainnet run independently. The testnet paves the way for the mainnet launch. Some projects leverage other blockchains to create their tokens. At the same time, they develop their mainnet. The matic network is a good recent example. Once the mainnet is launched, the old ERC-20 tokens are discarded, while the new ones are issued on the matic mainnet. We will take this example to see how this journey works.Matic Testnet 💥
In November 2019, Matic launched its public incentivized staking testnet event “Counter Stake”. Validators earned mainnet MATIC tokens by showcasing technical skills and by practicing and competing with other validators. Counter Stake had 3 stages: - Stage 0 – Setup. Date: November 2019
Action: All validators run the validator and block producer nodes, keep them synced with the given testnet, and understand the network. They also try deploying their testnet and experimenting with the code. - Stage 1 – Stake on the Beach Date: February 2020
Reward Pool: $40,000 worth of MATIC tokens Action: Stage 1 started with ~30 nodes. The Matic Foundation controlled a majority stake in the testnet in week 1 of the program. In the subsequent weeks, there was an increase in the validator slots. Stage 1 also provided a mechanism to replace poorly performing validators with those on the waitlist. The main testing features included are staking, unlocking rewards, penalties, and replacement strategies. - Stage 2 – The Grand Staking League
This is the final stage before the mainnet launch. Matic encouraged an all-out attack on the network at this stage.Matic Mainnet 💥
The matic mainnet went live on 31 May 2020. - Step #1: DApp partner onboarding, Genesis Ceremony & mainnet Go-Live with initial validator set (only Matic Foundation nodes and nodes run by select validators invited by the Matic team will be active).
- Step#2: Incremental Nodes (Onboarding 5-10 at a time). This is also with Matic foundation nodes.
- Step#3: Full release. Decentralized Release. Community Governance. 100+ Nodes.
Conclusion 👋
All core blockchain projects need to be evaluated based on the performance of the mainnet. Even then cryptocurrency mainnets are not the final products. There are repeated updates or revisions to a particular functionality. It is therefore very important to understand a project’s development road map and compare that with what has been achieved. Also, listen to comments from the project partners to evaluate how the partners are using the chain.
That's it for this article and in the next blog posts we'll be exploring more blockchain topics and I hope y'all got some learnings from it.
